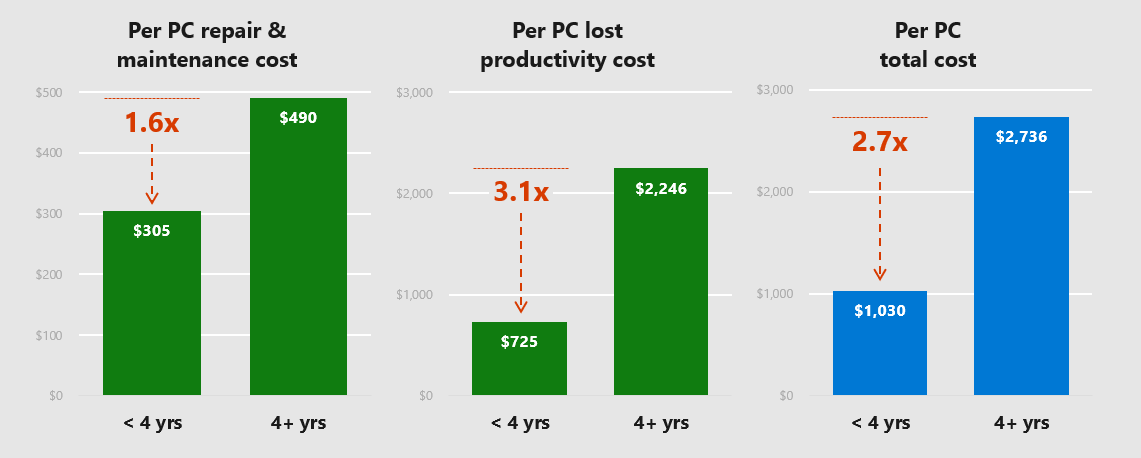
Increasing profitability, improving workforce productivity and reducing operational costs are among the top five business issues for SMBs in the Asia/Pacific region. Cost is sometimes a tricky item to nail down as too often SMBs focus on short term costs. In most cases this approach is absolutely valid but it can lead to situations that cost them more. The choice between maintaining older PCs and replacing them with newer PCs is one such area. Techaisle, conducted a Pan-Asia survey of 2156 SMBs in five countries to understand the comparative differences in costs of maintaining older & newer PCs and associated quantifiable productivity lost and the impact of newer PCs. Findings from the survey, commissioned by Microsoft & Intel, and driving Microsoft’s “Make the Shift Campaign” in the Pan-Asian region, uncovers that the cost of upkeeping a PC older than four years can be used to purchase at least two new Modern PCs.
The study reveals that the cost of owning a 4 year or older PC by an SMB is US$2,736 which is 2.7 times the cost for a PC that is less than 4 years old. The study also revealed that an average of 112 hours is lost due to downtime of an older PC, a number that is 3.1X of newer PCs. This is a “stealth” cost that drains cash flow and adds to the operating cost of an SMB which they can hardly afford. Cost implications vary for SMBs of different sizes.