Internet and the web are the navigation routes that we have been developing since the 1970s; the always-on, everywhere-connected Interwork platform is the destination that we will be creating in 2018 and for years to come.
As we enter 2018, it seems that online capabilities and activities are entering a new era. There are still advances to be made in the ‘net’ realm: there is constant pressure to expand the speed of the Internet, enabling it to handle the voracious demands of unstructured content like video, and the rise of IoT portends a coming tsunami of data from billions of connected devices. However, the key focus of web-based business investment is now less about the ‘net’ and more about the ‘work’: the ways that an increasingly-connected world supports pursuit of previously-unattainable objectives. The most important IT-related development in 2018 will be this focus on connectedness – connected cloud, connected edge, connected applications, connected security, conected collaboration, connected workspaces and connected insights. (Download your free white paper here)
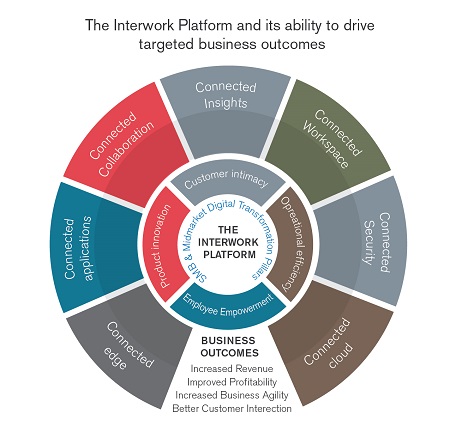
Techaisle calls it the “Interwork platform” (as described in Techaisle's latest white paper). This refers to Techaisle’s belief that 2018 will mark a transition point at which corporate focus on developing and deploying systems that offer the capacity to connect diverse resources (the Internet platform) will be surpassed by a focus on capitalizing on the benefits of connected information, assets and users and teams – the ‘Interwork platform’ - to deliver on the four pillars of digital transformation: operational efficiency, customer intimacy, employee empowerment and innovation.
In the early 1970s, computer science pioneers Vint Cerf and Robert E. Kahn developed the networking protocol TCP/IP – Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol – which enabled interconnections between networks to form a ‘network of networks’. Fifteen years later, in 1989, Tim Berners-Lee developed the World Wide Web, allowing browsers to follow hypertext links to far-flung resources. The Web was released to the general public in August 1991 – and businesses and individuals around the world have spent more than 25 years developing a vast array of content, process and interactive capabilities that are set within and rely on the network of networks.
Techaisle’s position is that from the perspective of the technology world, 2018 – and quite possibly, several years following 2018 – will be defined by the benefits arising from the interconnection of all types of resources: platforms/environments, information, devices and applications. With the connective fabric now (or rapidly becoming) ubiquitous, businesses of all types and sizes will move beyond a focus on network access, and concentrate instead on using Interwork technologies to drive progress across the four pillars of digital transformation: operational efficiency, customer intimacy, employee empowerment and product innovation.
Techaisle’s recent point-of-view on the Interwork platform highlights seven key areas and trends playing out across seven key technology areas:
- Connected cloud, which provides the foundation for Interwork, the bedrock on which Interwork platforms are built
- Connected edge, which completes that foundation and will work with connected cloud to deliver the ‘yin and yang’ of the Interwork platform’s infrastructure
- Connected applications, that represent the best path forward for corporate workloads and processes – and represent a critical component of the Interwork platform
- Connected security, is an essential property of the Interwork platform as security strategies no longer resemble a ‘wrapper’ around assets
- Connected collaboration, as it becomes part of the fabric of business activity, rather than as a means of enabling connections between discrete tasks
- Connected workspaces, which draw together assets and users, delivering increased benefit within each category while simultaneously extending and strengthening the core of the Interwork platform; and
- Connected insights, the information gained/accessed through the platform, which enables businesses to address constantly-advancing expectations for speed (of operational decisions) and completeness (of strategic decisions).
Business and IT executives who are able to grasp the benefits associated with these seven key areas – and who are able to profit from the points at which multiple connected business resources combine to build the broader Interwork platforms – will emerge as leaders in and beyond 2018. Their organizations will participate in shaping rapidly-evolving business and consumer expectations for responsiveness and agility. Businesses that capitalize on Interwork capabilities will capture preferred positions within their markets, and within the millennial labor pool that defines a key area of near-term competition.
There are many powerful rationales for investing in each of the seven components of an Interwork platform, and as Techaisle's white paper demonstrates, each component in turn delivers greater value when it is connected with the other links in the Interwork chain.
Download your free white paper here
















